ESTIMATIVA DA DIFUSIVIDADE TÉRMICA DE LIGAS METÁLICAS UTILIZANDO UM CAMPO DE TEMPERATURA PERIÓDICO
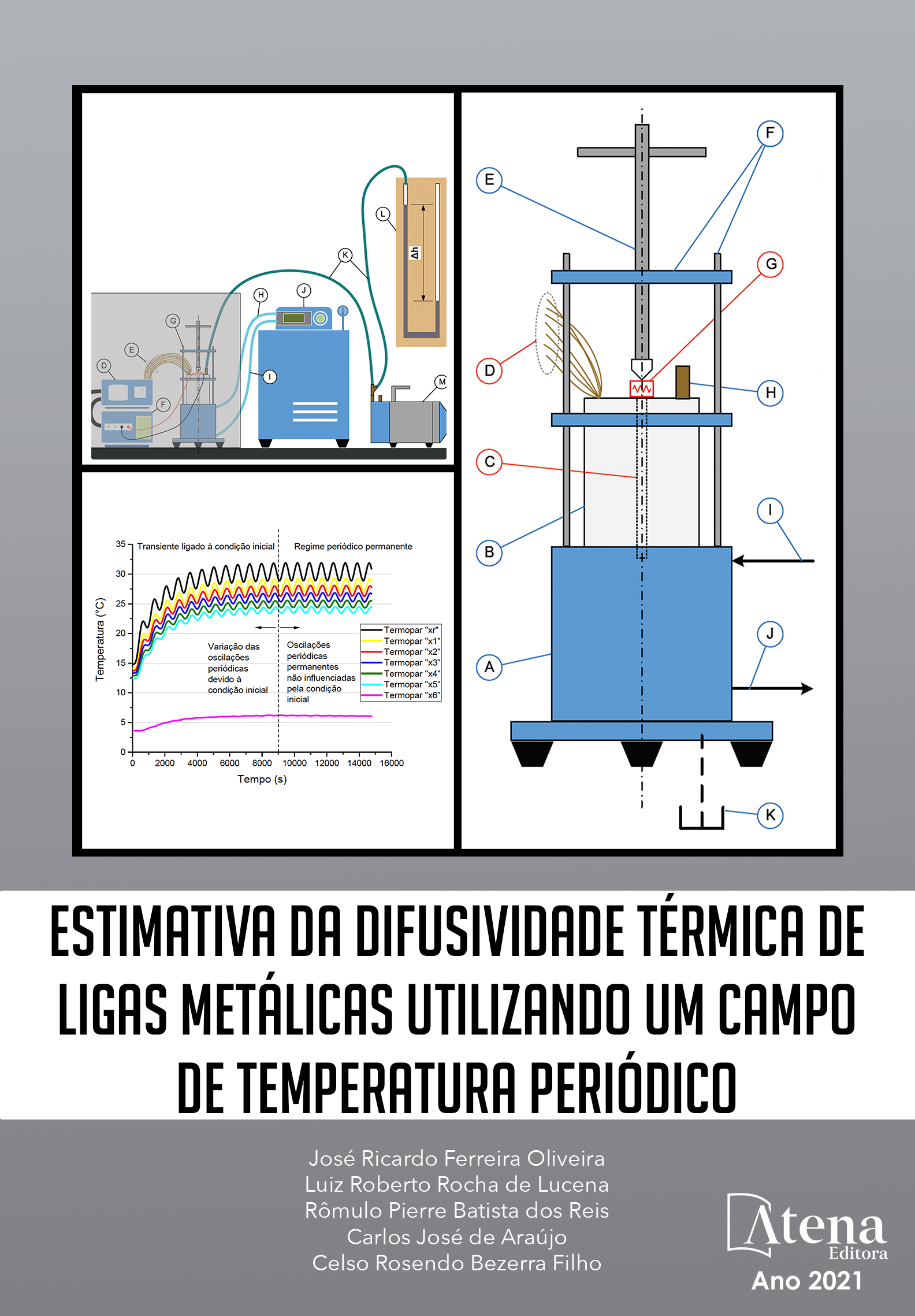
A caracterização termofísica dos materiais utilizados na Engenharia é de grande importância para realização de projetos nas mais diversas áreas de conhecimento onde os fenômenos ligados aos processos de transferência de calor exercem um papel fundamental. A difusividade térmica é uma propriedade termofísica importantíssima na análise de problemas de difusão de energia térmica. Este trabalho teve como proposta a determinação desta propriedade utilizando um campo de temperatura periódico. Para isto, foi construído um dispositivo experimental com princípio de funcionamento no método de Angstrom, o qual faz uso de um fluxo de calor periódico de uma fonte controlada, gerando assim, um campo de temperatura periódico na amostra em teste. Termopares foram instalados nas amostras para captar os sinais de temperatura gerados pelo fluxo de calor periódico. A amplitude e a fase destes sinais foram obtidas por meio de um software de análise gráfica. O termopar mais próximo da fonte de calor foi adotado como referência, ao passo que a razão de amplitudes e a defasagem, entre os sinais térmicos registrados pelos demais termopares em relação ao registrado por àquele termopar, foram calculadas. Estes resultados foram utilizados em modelos matemáticos para determinar a difusividade térmica, que pode ser identificada ou através da razão de amplitudes ou através da defasagem entre os perfis de temperatura. As amostras utilizadas neste trabalho foram de aço inox AISI 304 e aço inox AISI 316. Os valores de difusividade térmica identificados para estes materiais, quando foram comparados com valores disponíveis na literatura, obtiveram uma boa concordância, tendo em vista a faixa de incerteza apresentada.
ESTIMATIVA DA DIFUSIVIDADE TÉRMICA DE LIGAS METÁLICAS UTILIZANDO UM CAMPO DE TEMPERATURA PERIÓDICO
-
DOI: 10.22533/at.ed.128212705
-
Palavras-chave: Difusividade Térmica. Propriedades Termofísicas. Campo de Temperatura Periódico. Método de Angstrom. Dispositivo Experimental.
-
Keywords: Thermal Diffusivity. Thermophysical Properties. Periodic Temperature Field. Angstrom’s Method. Experimental Device.
-
Abstract:
Thermophysical characterization of materials used in engineering is very important for realization of projects in the most diverse areas of knowledge where the phenomena related to the process of heat transfer play an important role. Thermal diffusivity is a very important thermal property on the analysis of problems of diffusion of thermal energy. This work proposes the determination of this property using a periodic temperature field. For this, an experimental device was built with principle of operation in Angstrom’s method, which makes use of a periodic heat flow from a controlled source, thereby generating a periodic temperature field in the test sample. Thermocouples were installed on the samples for capture of signals generated by the periodic heat flow. Amplitude and phase of these signals were obtained by means of graphic analysis software. The thermocouple closest to the heat source was adopted as reference, and the ratio and phase lag, between the thermal signals registered by other thermocouples in relation to that registered by that thermocouple, were calculated. These results were utilized in mathematical models to determine the thermal diffusivity, whose identification can be performed either through the amplitude ratio or through the phase lag between the temperature profiles. Samples utilized in this work were stainless steel AISI 304 and stainless steel AISI 316. Thermal diffusivity estimative, when compared whit values available in literature obtained a good agreement, considering the range of uncertainty presented.
-
Número de páginas: 55
- LUIZ ROBERTO ROCHA DE LUCENA
- RÔMULO PIERRE BATISTA DOS REIS
- CARLOS JOSÉ DE ARAÚJO
- CELSO ROSENDO BEZERRA FILHO
- José Ricardo Ferreira Oliveira


